What Is Impotence?
Impotence is a condition that consistently affects a person’s ability to maintain or achieve an erection, or ability to achieve ejaculation. It’s a form of (ED) erectile dysfunction.
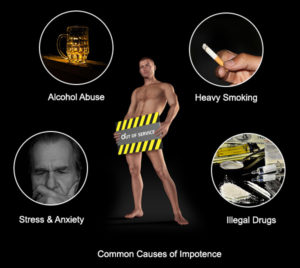
There can be several participating factors for impotence. These include both physical & emotional dis-orders. According to The Merck Manual, an estimated 50% of men age between 40 to 70 experience some ED at one time or another. The risk of impotence increases with age wise.
It’s also been noted that men with more education are not more likely to experience impotence, perhaps because they have healthier lifestyles on average or below average.
Impotence often has a negative affect on sexual life, and can cause additional stress, depression, and low self-esteem.
Understanding the most common potential causes can help a person identify why they may be experiencing the condition.
1. Endocrine Diseases
The body’s endocrine system produces hormones which regulate metabolism, sexual function, reproduction, mood, and much more.
Diabetes is an example of an endocrine disease that can cause a person to experience impotence. Diabetes affects the body’s ability to utilize the hormone insulin. One of the side effects associated with chronic diabetes is nerve damage. This affects penis sensations. Other complications associated with diabetes are impaired blood flow and hormone levels. Both of these factors can contribute to impotence.
2. Neurological and Nerve Disorders
Several neurological conditions can increase the risk for impotence. Nerve condition affect the brain’s performance to communicate with the reproductive system. This can prevent a person from achieving an erection.
Neurological disorders associated with impotence include:
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Parkinson’s disease
- brain or spinal tumors
- multiple sclerosis
- stroke
- temporal lobe epilepsy
People who have had prostate gland surgery can also experience nerve damage that causes impotence.
Long distance bicycle riders can also experience temporary impotence. This is because repeated pressure on the buttocks and genitals can affect the function of the nerves.
3. Taking Medications
Taking certain medications can affect blood flow, which can lead to ED. A person should never stop taking a medicine without their doctor’s permission, even if it’s known to cause impotence.
Examples of medications known to cause impotence include:
- alpha-adrenergic blockers, including tamsulosin (Flomax)
- beta-blockers, such as carvedilol (Coreg) and metoprolol (Lopressor)
- cancer chemotherapy medications, such as cimetidine (Tagamet)
- central nervous system depressants, such as alprazolam (Xanax), diazepam (Valium), and codeine (found in various brand name drugs)
- central nervous system stimulants, such as cocaine or amphetamines
- diuretics, such as furosemide (Lasix) and spironolactone (Aldactone)
- selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or SSRIs (Prozac, Paxil)
- synthetic hormones, such as leuprolide (Eligard)
4. Cardiac-Related Conditions
Conditions that affect the heart and its ability to pump blood well can cause impotence. Without enough blood flow to the penis, a person can’t achieve an erection.
Atherosclerosis, a condition that causes the blood vessels to become clogged, can cause impotence. High cholesterol and high blood pressure (hypertension) are also associated with increased risks for impotence.
5. Lifestyle Factors and Emotional Disorders
To achieve an erection, a person must first go through what’s known as an excitement phase. This phase can be an emotional response. If a person has an emotional disorder, this affects their ability to become sexually excited.
Depression and anxiety are associated with increased risk for impotence. Depression is a feeling of sadness, loss of hope, or helplessness. Fatigue related to depression can also cause impotence.
Performance anxiety can be another cause of impotence. If a person wasn’t able to achieve an erection in the past, he may fear he won’t be able to achieve an erection in the future. A person may also find he can’t achieve an erection with a certain partner. Someone with ED related to performance anxiety may be able to have full erections when masturbating or when sleeping, yet he isn’t able to maintain an erection during intercourse.
Abuse of drugs like cocaine and amphetamines can also cause impotence. Alcohol abuse and alcoholism can affect a person’s ability to achieve or maintain an erection as well. See your doctor if you suspect that you may have a substance abuse problem.

root india healthcare
impotent
Treatment
Treatments are available for impotence, including prescription medications, natural remedies, and lifestyle changes.
Prescription Medications
There are a variety of medical treatments that can be used to treat impotence. Prescription treatments and other medical interventions to help treat impotence include:
- sidenafil (Viagra)
- tadalafil (Cialis)
- vardenafil (Staxyn, Levitra)
- testosterone replacement
- blood vessel surgery
- psychological counseling
Natural Remedies
For those who want to avoid prescription medication, there are a variety of natural remedies known to help treat impotence.
Some natural or alternative remedies for impotence include:
- acupuncture
- ginseng
- pomegranate juice
Before you use any natural remedies, make sure that you consult your doctor first.
Lifestyle Changes
Whether a person’s impotence has a physical or an emotional cause, there are many cases where lifestyle changes can reduce their struggle with ED.
According to the several Specialist , these lifestyle and behavior changes include:
- smoking and drinking less
- strengthening communication in a romantic relationship
- reducing anxiety
- exercising more and following a healthy diet
Prevention
Impotence has a huge number of causes, but there are still measures you can take to help prevent it.
Methods of possible prevention include:
- taking part in physical exercise, which decreases the risk of impotence
- avoiding smoking, drugs, or alcohol abuse
- getting enough sleep
- following a healthy diet
- reducing stress, anxiety, and depression
Outlook
Impotence can change a person’s life and affect their self-admiration. Although aging is often associated with erectile dysfunction, growing older isn’t necessarily one of the biggest causes of impotence. ED isn’t considered a natural part of aging. Aging is just a risk factor. Some never struggle with impotence.
Though erectile dysfunction can have a negative impact on sex life, it’s a treatable condition. Many interventions exist that can help a person regain their sexual function, including natural remedies, medications, and lifestyle changes.
Because impotence can signal an underlying health problem, make an appointment with your doctor if it becomes a consistent problem, even if you think it’s just stress.
for more information write to us : Radhika@rihl.in || Root India Healthcare || www.rihl.in ||